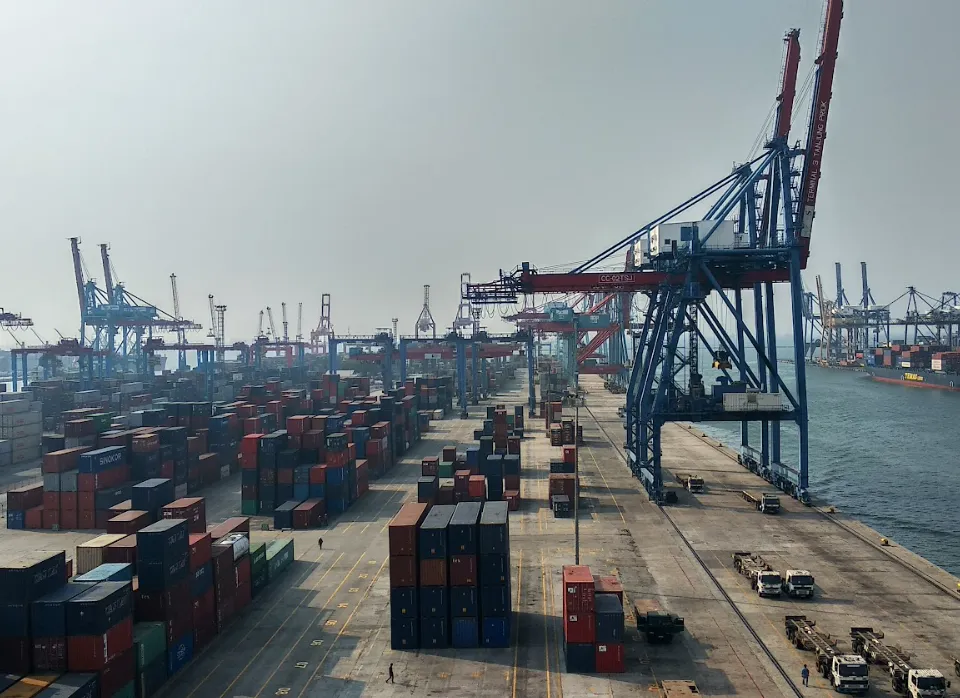
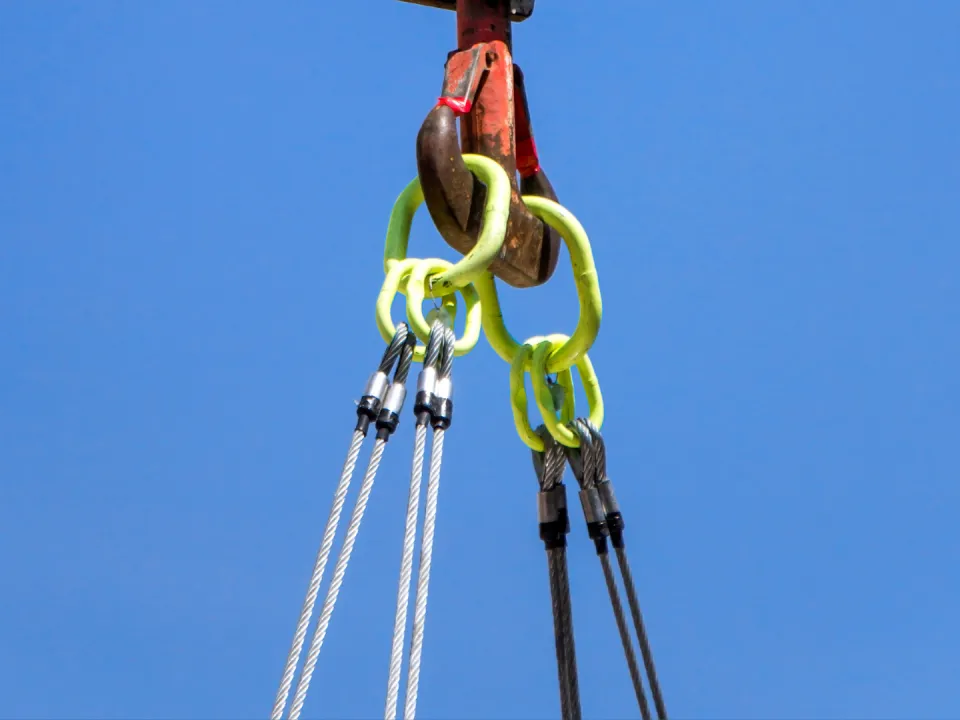
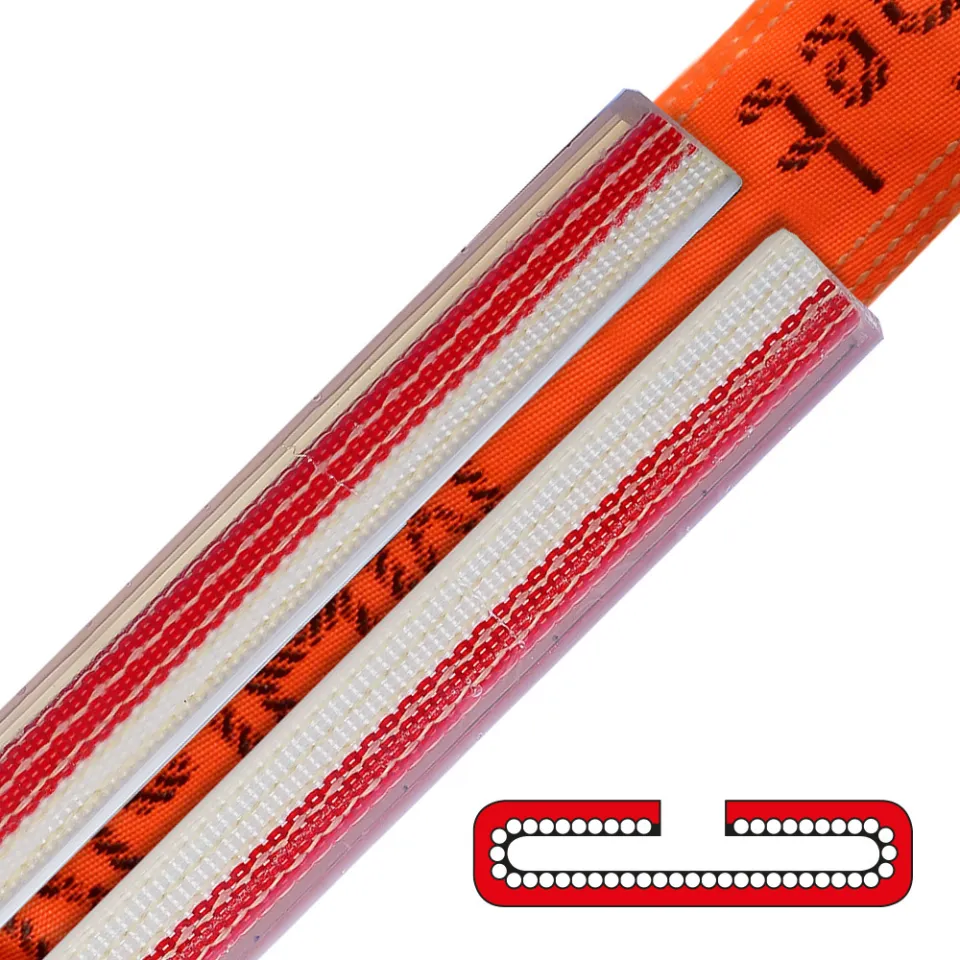
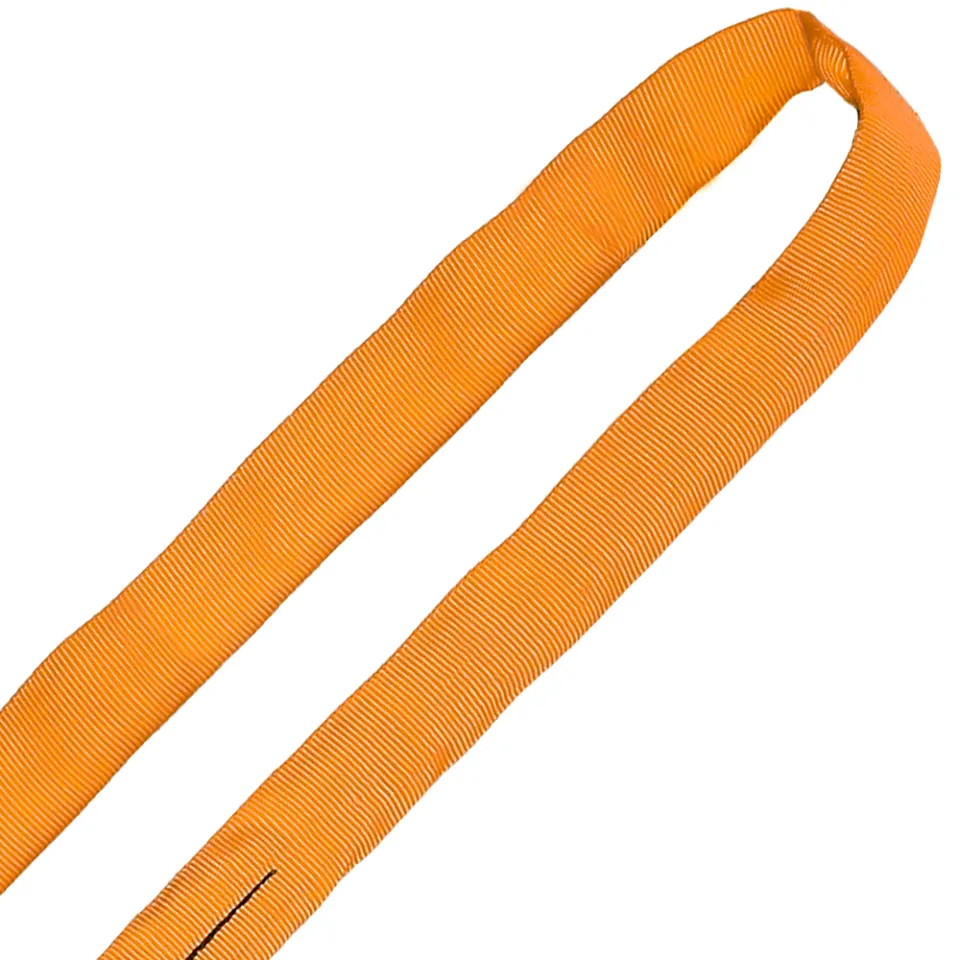
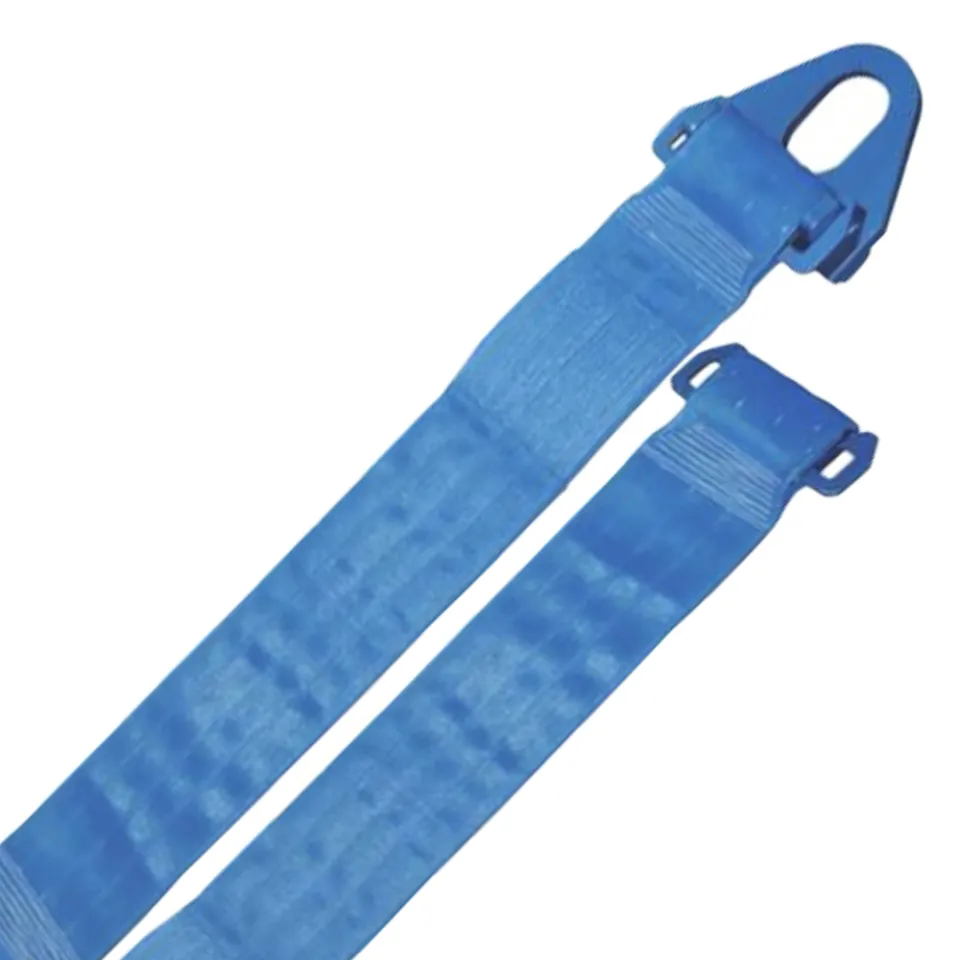
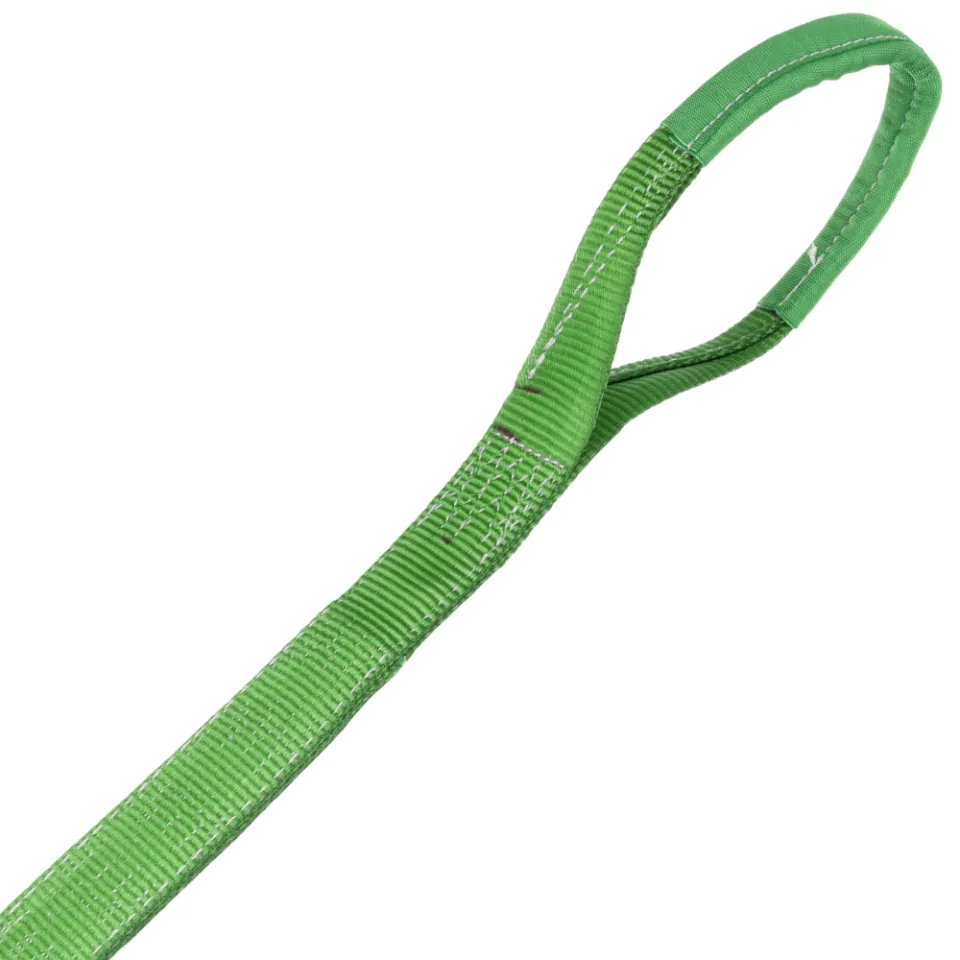
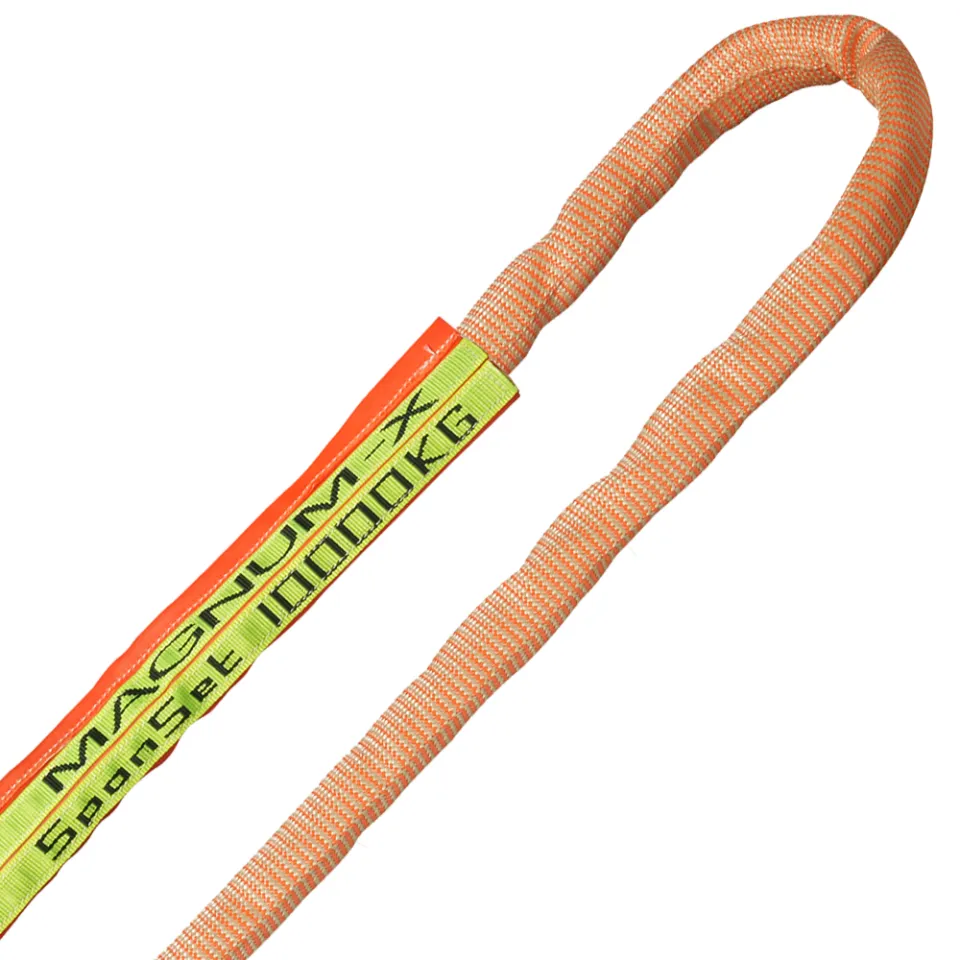
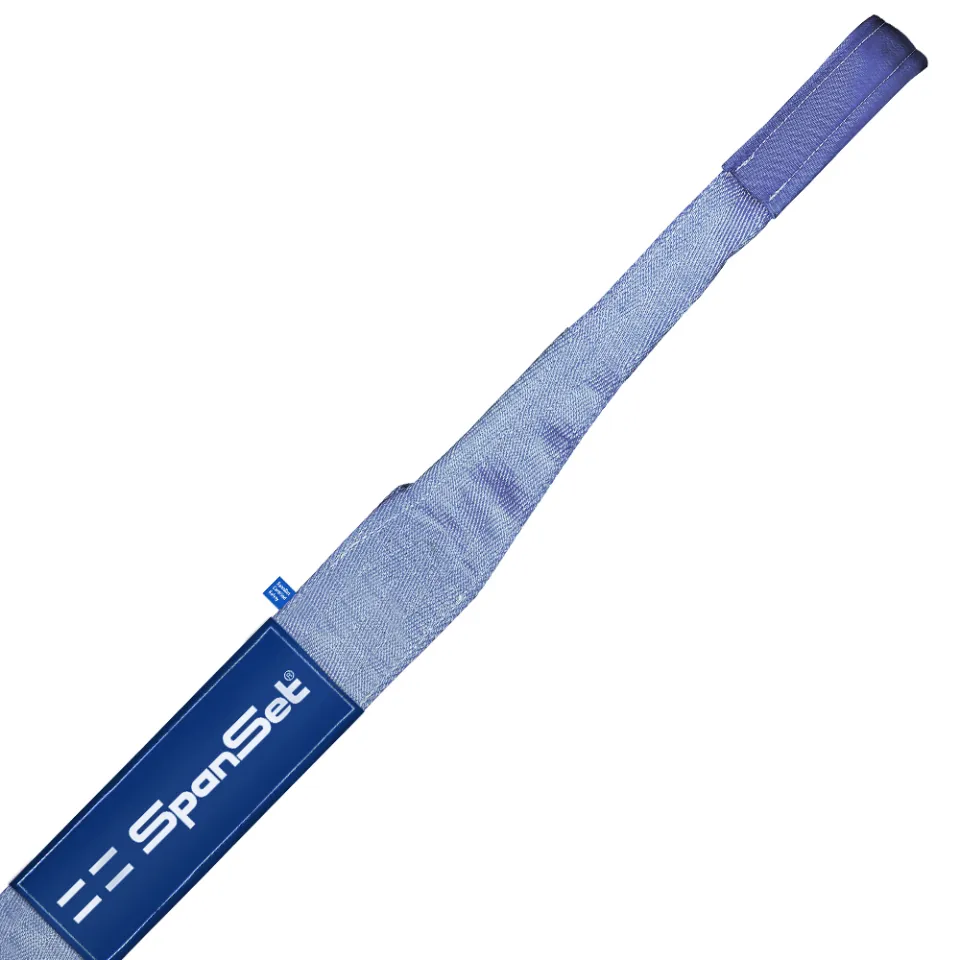
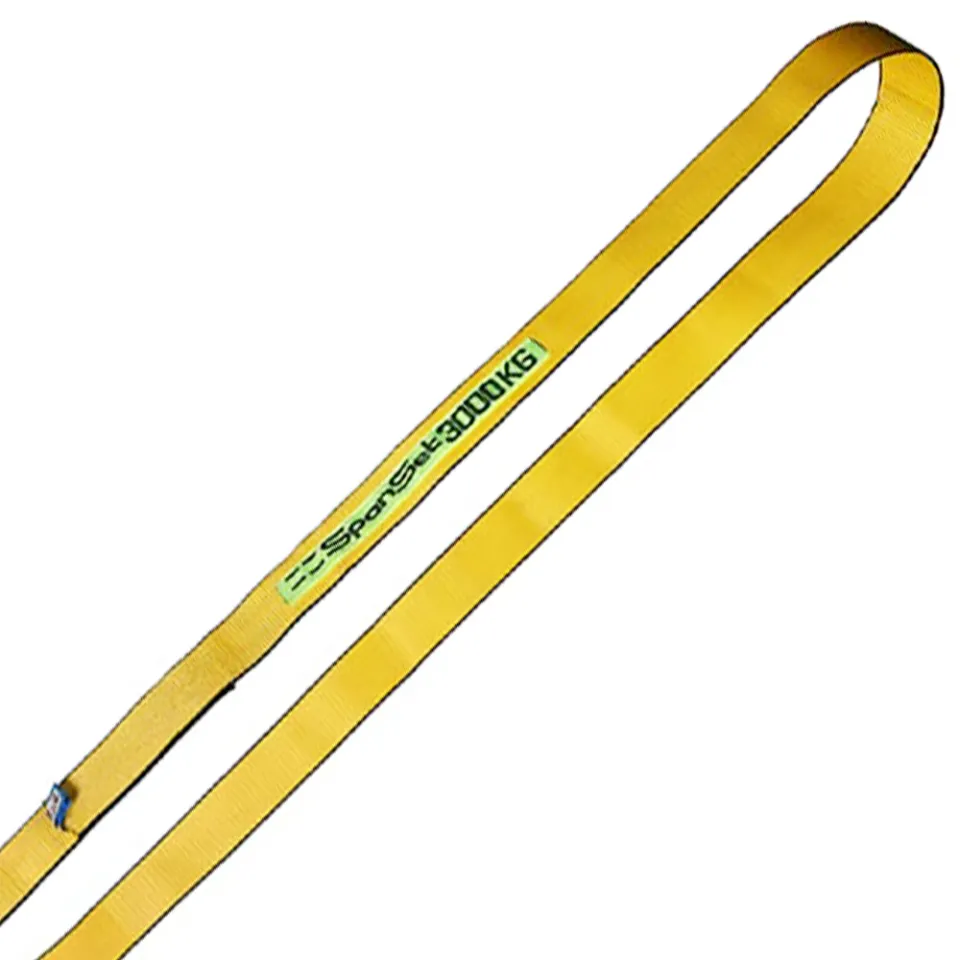
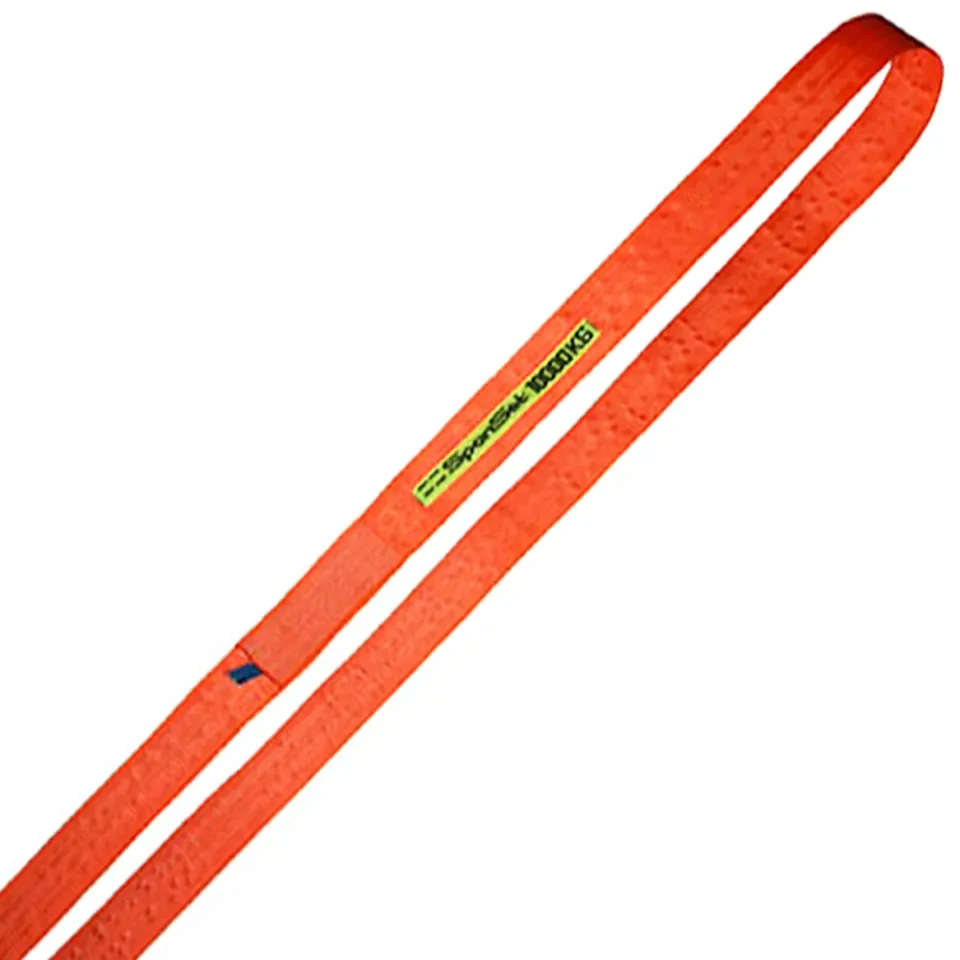
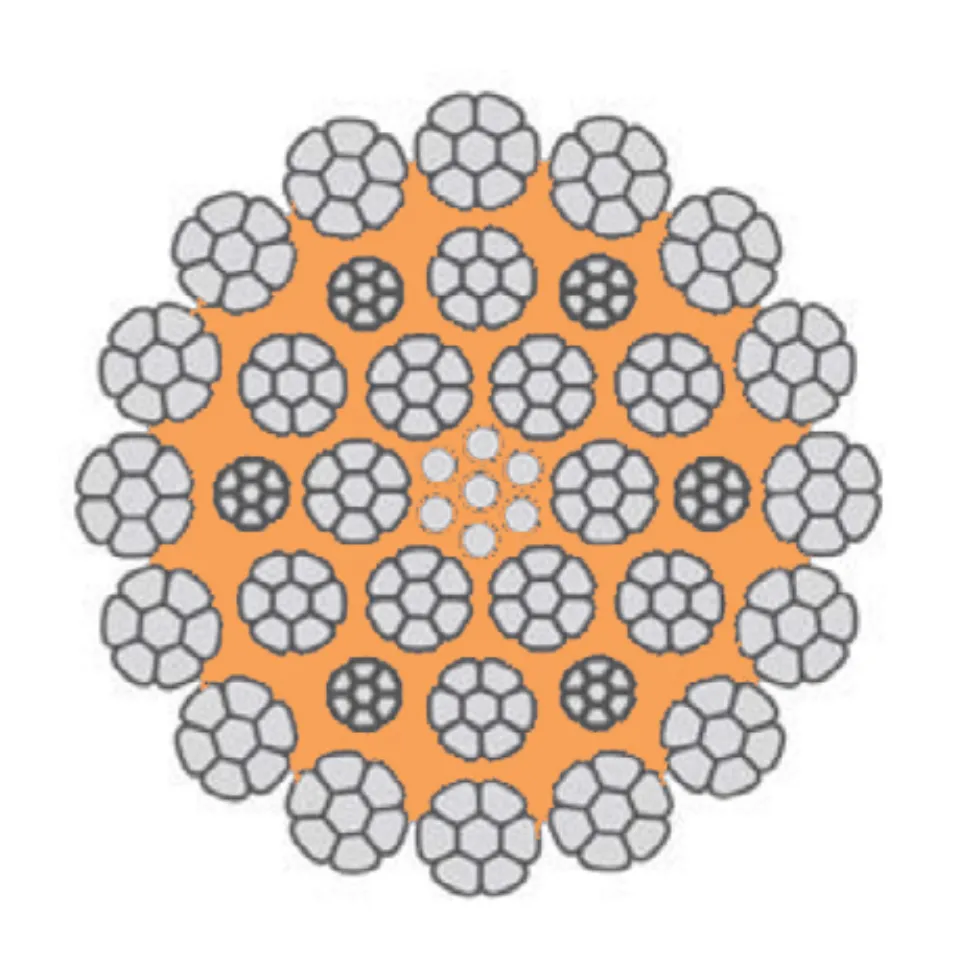
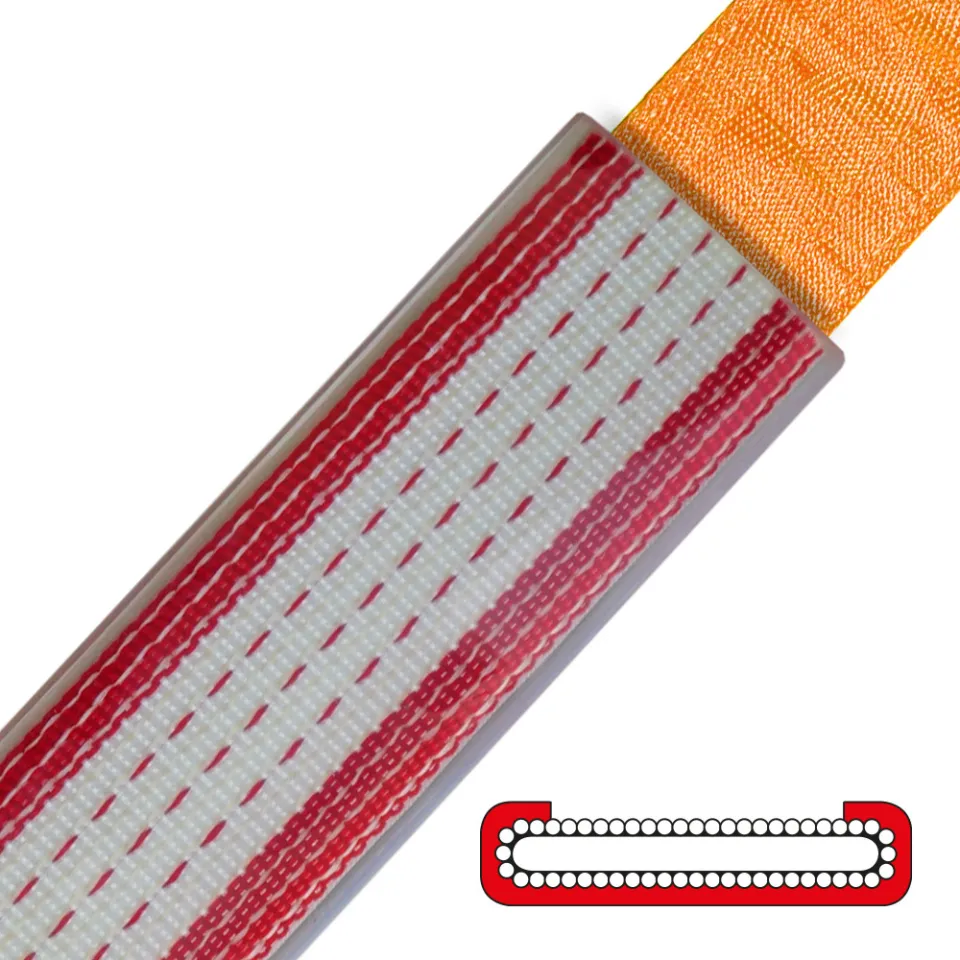
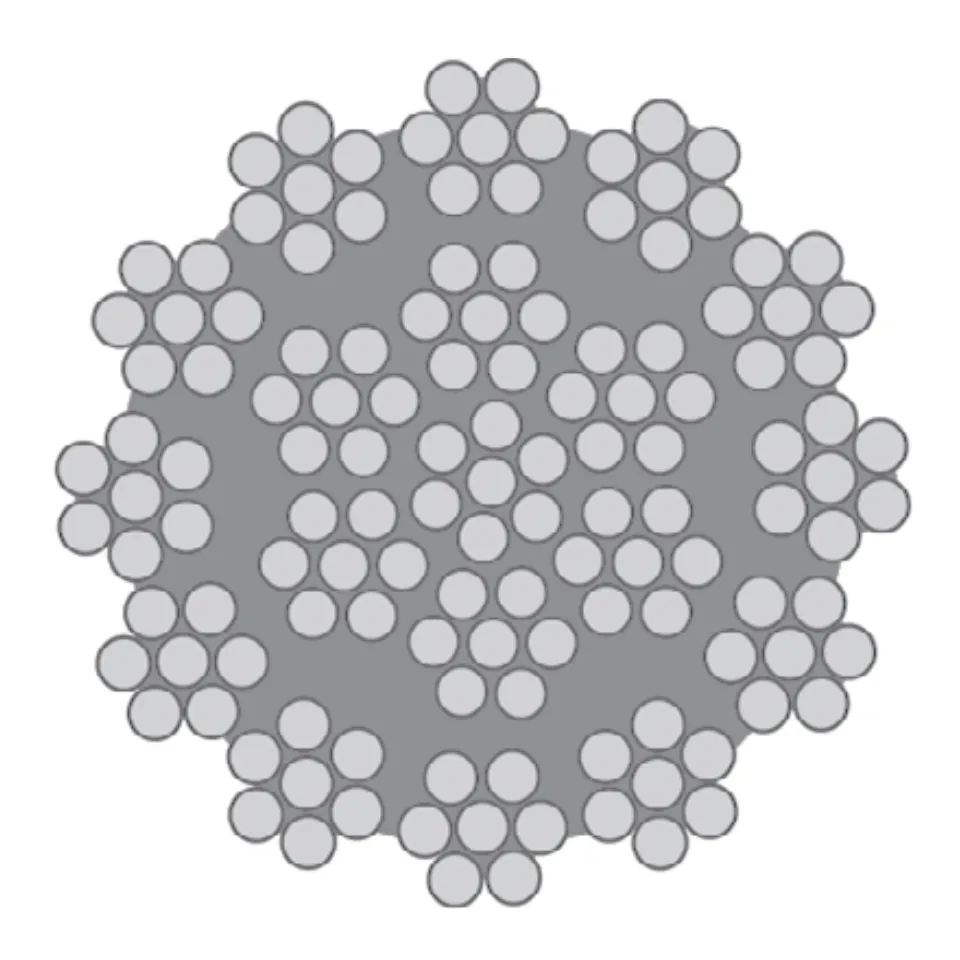
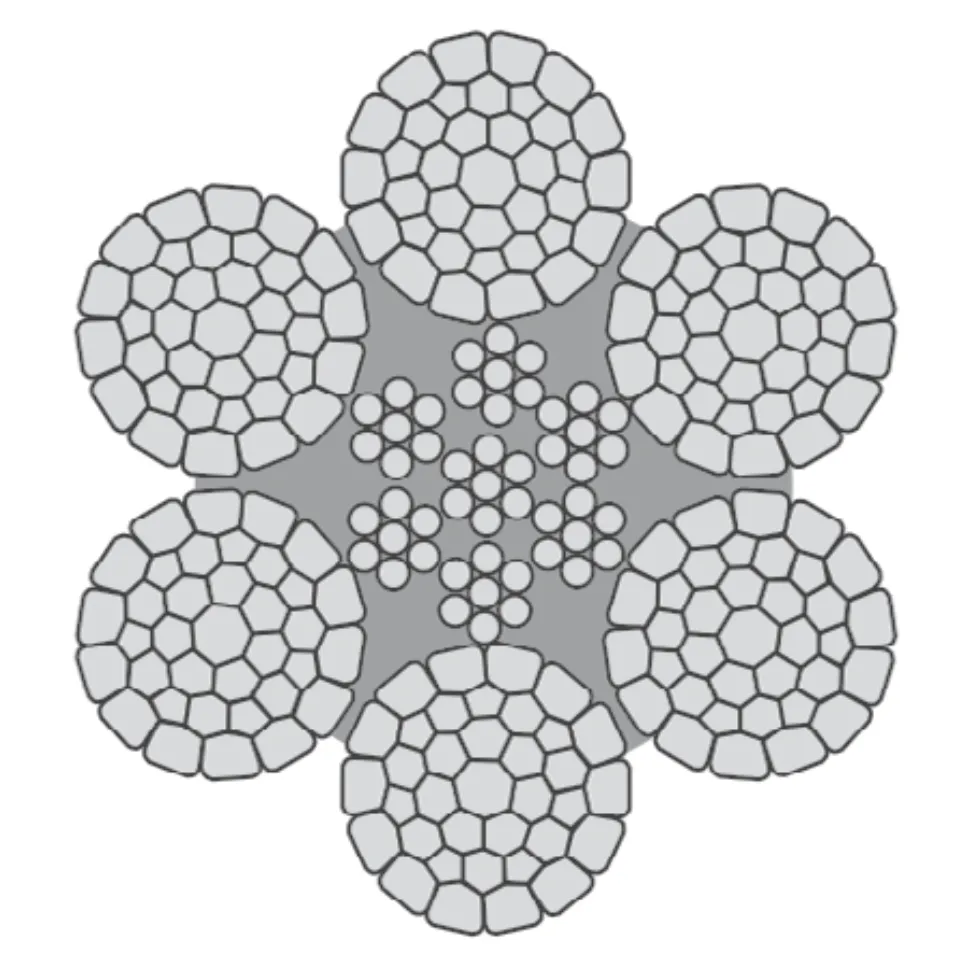
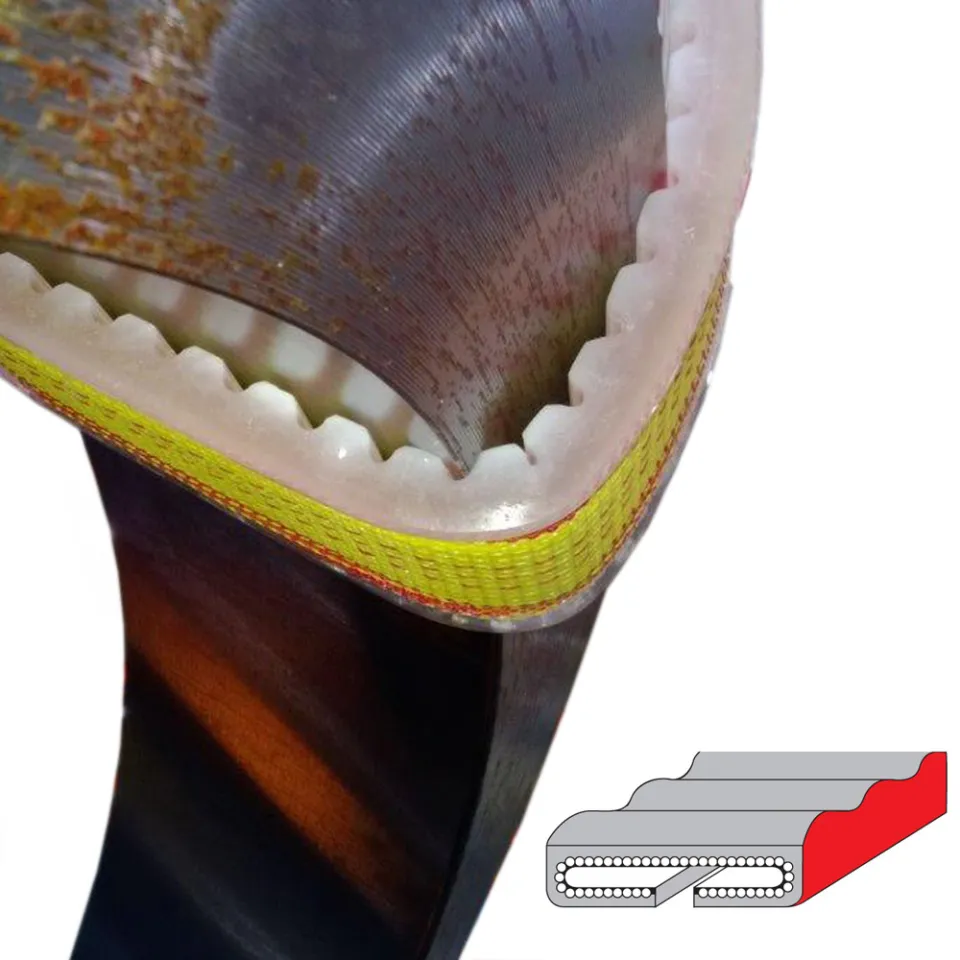
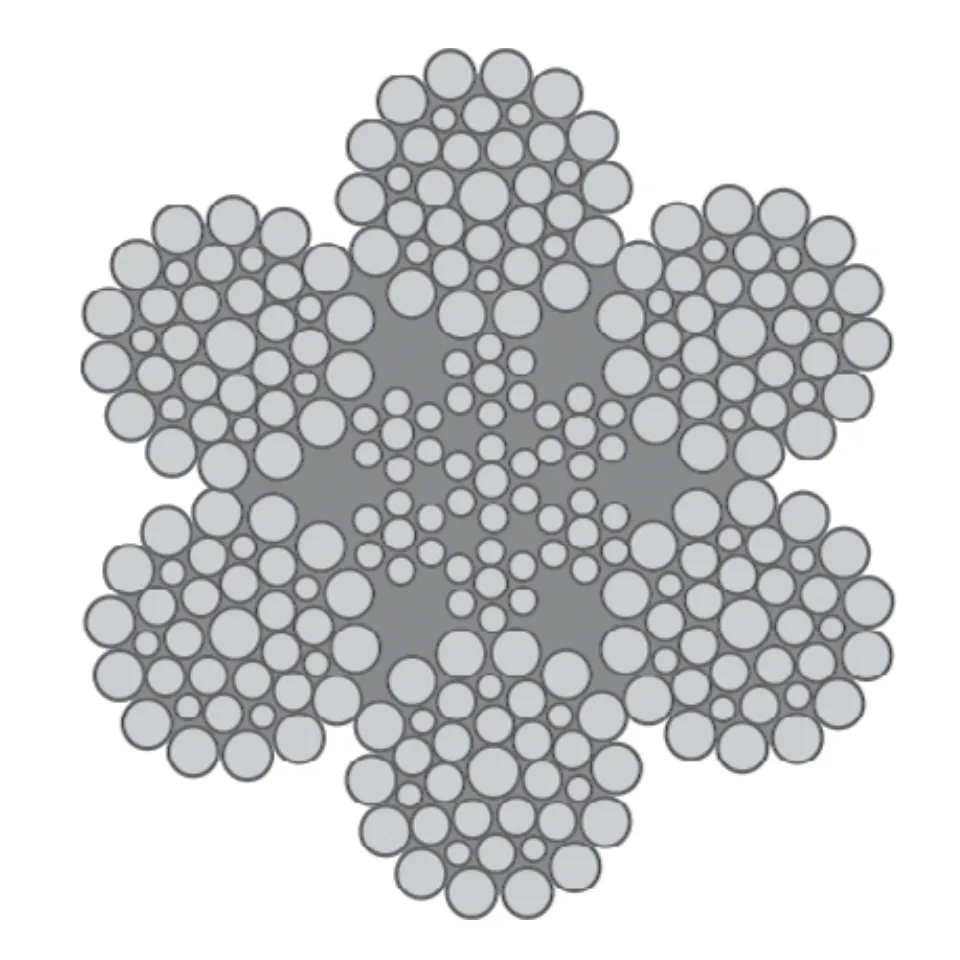
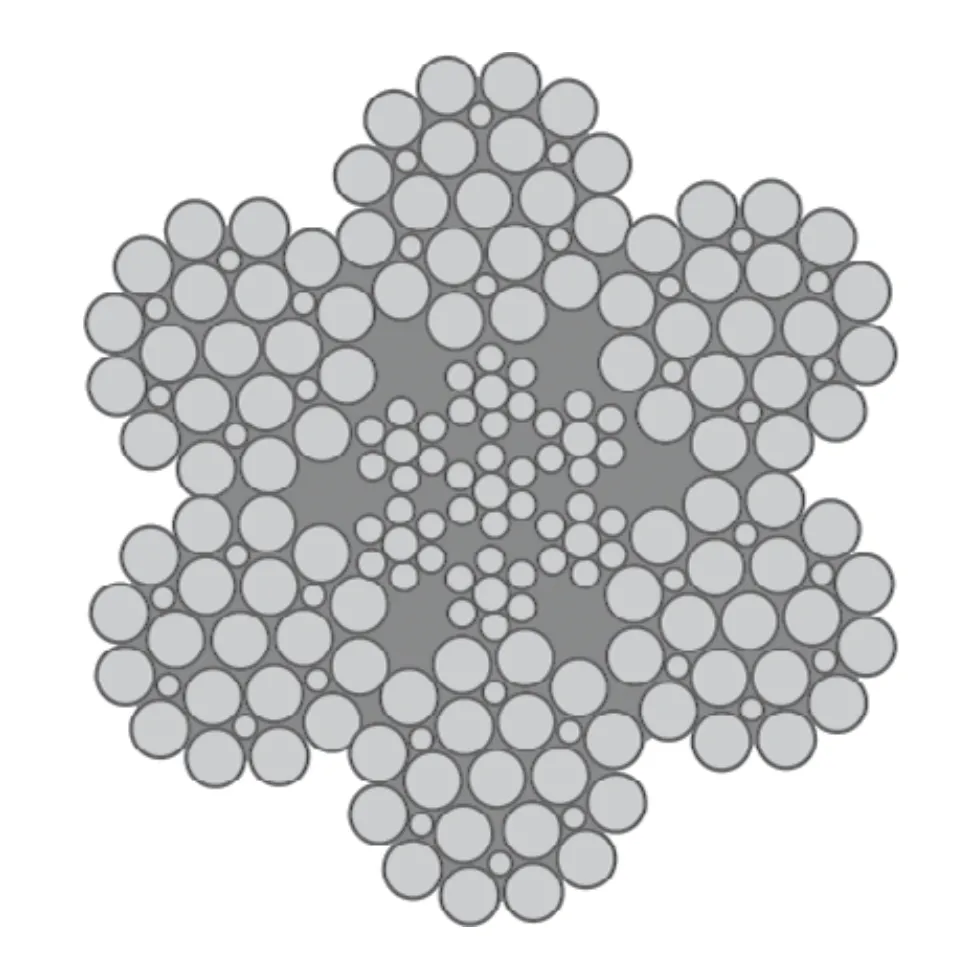
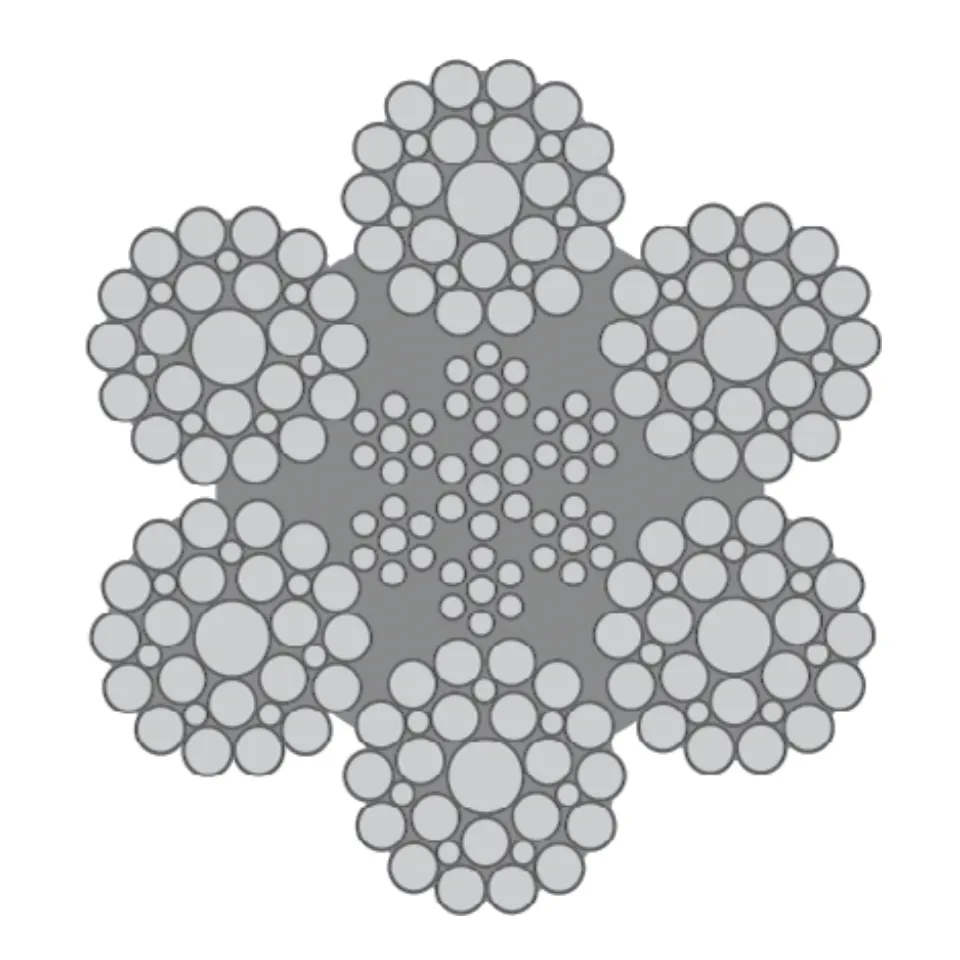
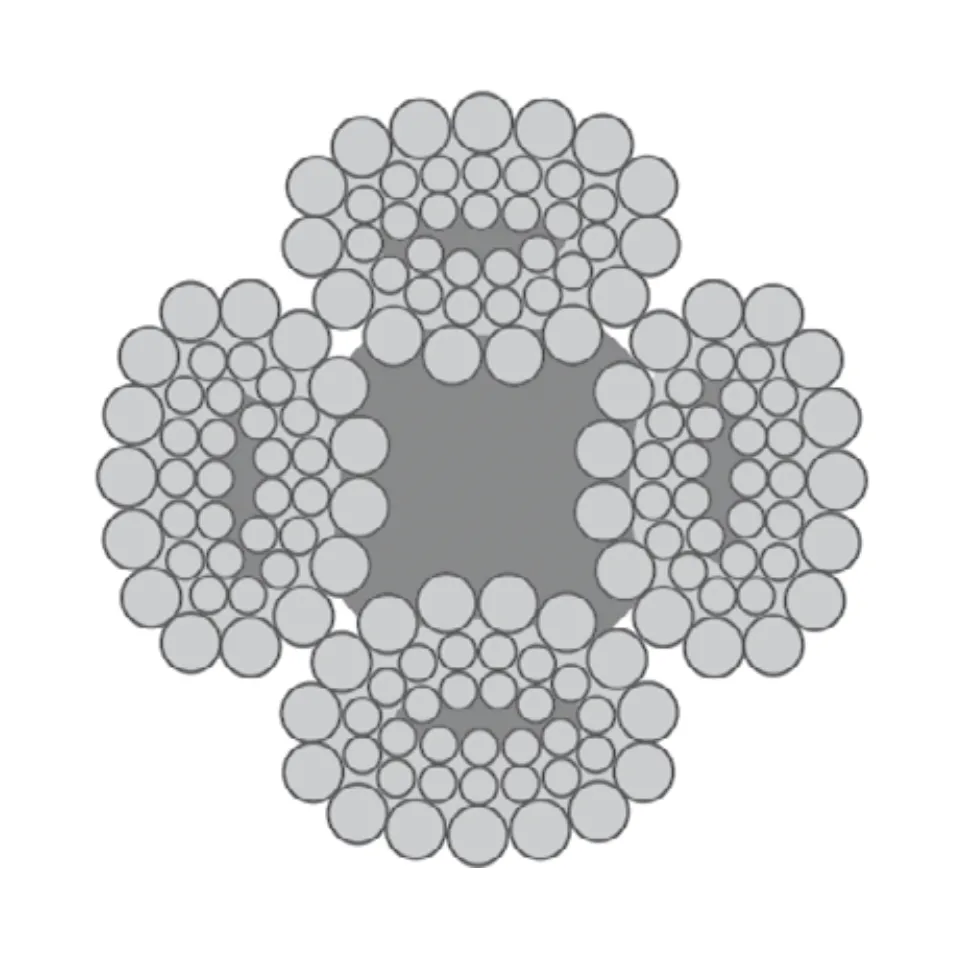
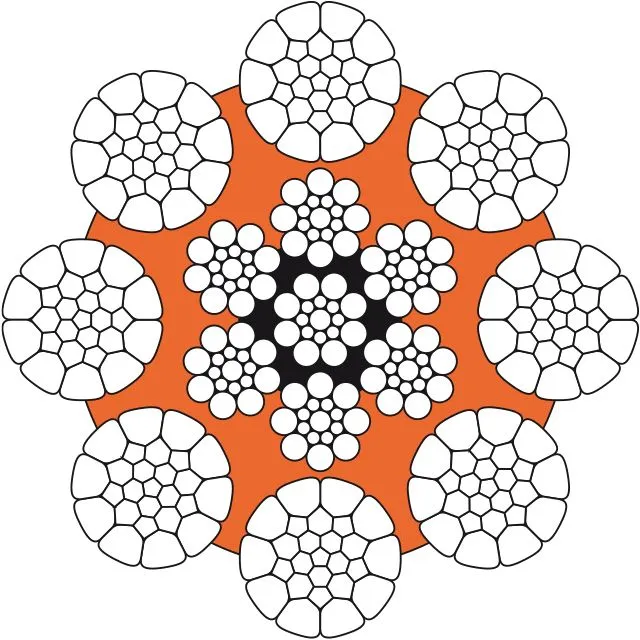
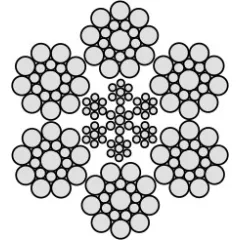
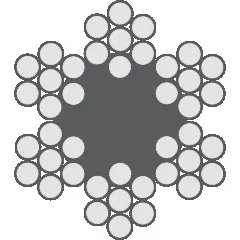
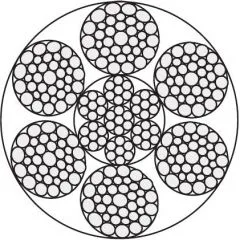
Differences Between Wire Rope Sling and Webbing Sling
There are two types of slings that are most commonly used, wire rope slings and webbing slings. This...
Get to Know Wire Rope and its Functions in Various Industries
Wire rope is a rope made of wire that has high strength to withstand heavy loads. Here are its...
Wire Rope IWRC: What Does It Mean? Find Out Here!
Wire Rope IWRC is a type of wire rope that is popular for its strength and durability. Learn more...
Wire Rope Breaking Load: Meaning & Calculation
The breaking load is the maximum tensile force a wire rope can withstand before failure. It depends...
How to Measure Wire Rope Size Correctly
The size of a wire rope affects lifting strength. Learn the correct way to measure wire rope...
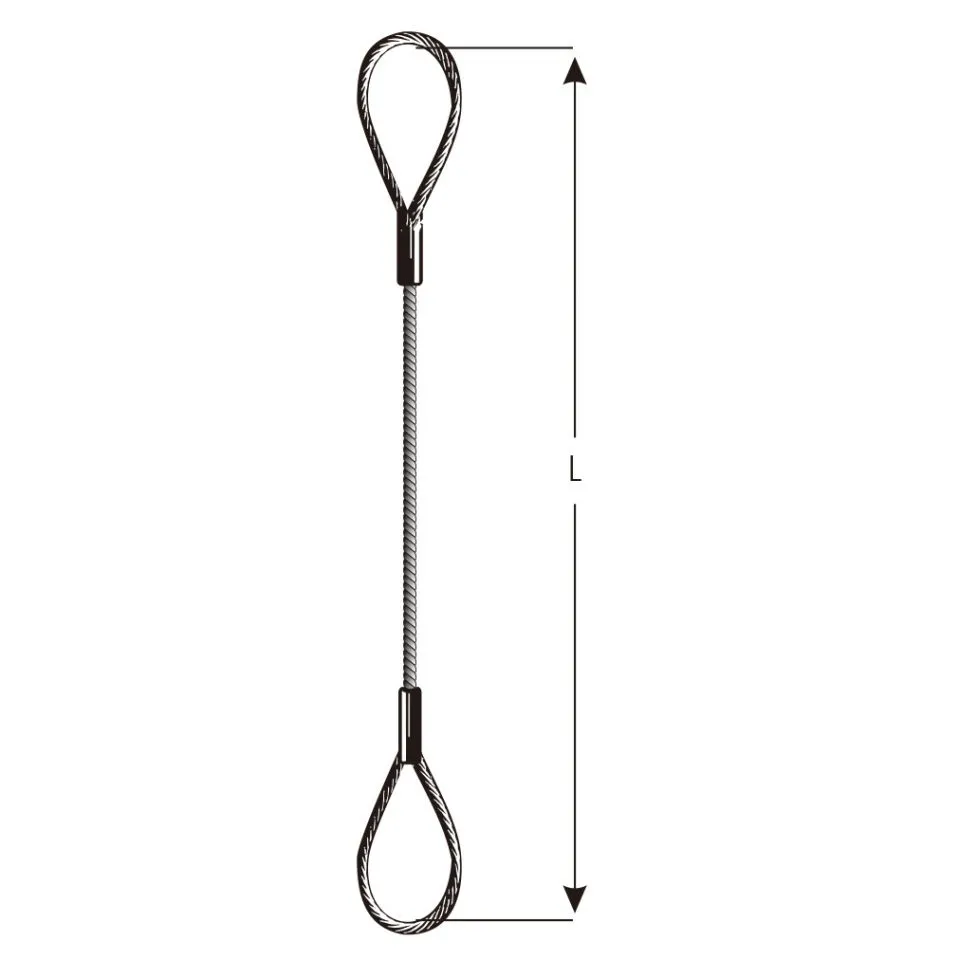
Copy of Types of Wire Rope Slings and Their Applications
Guide to selecting wire rope accessories like shackles, sockets, and clips. Ensure safe and...
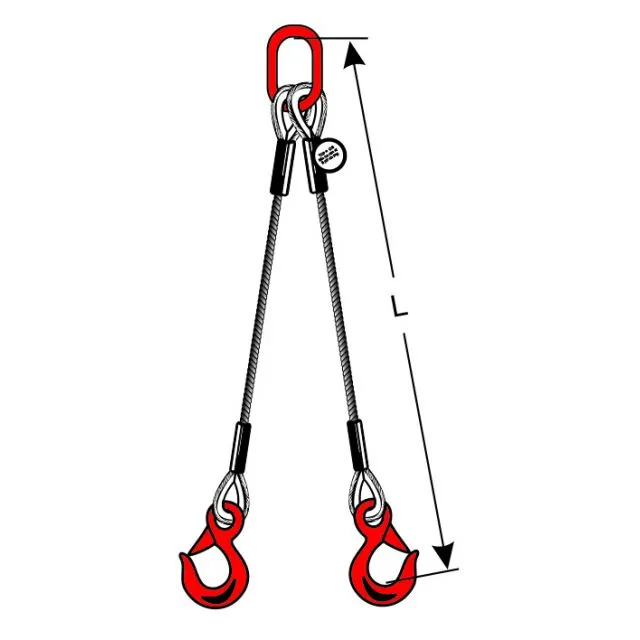
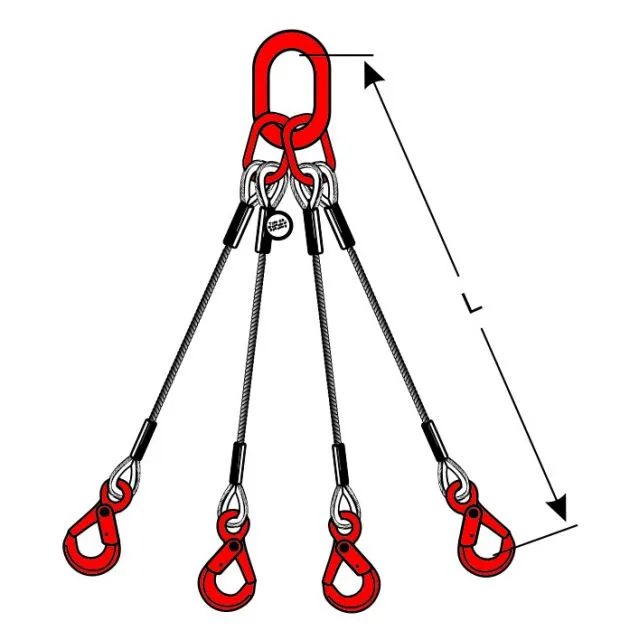
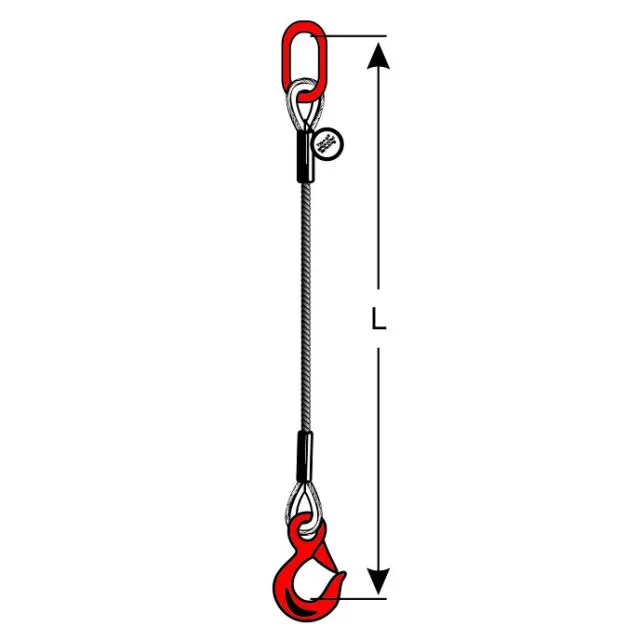
Types of Wire Rope Slings and Their Applications
Learn the different types of wire rope slings like eye & eye, endless, and bridle slings. Find the...
Types of Wire Rope Damage & How to Prevent Them
Discover common wire rope damage—rust, broken wires, diameter reduction, and more—and learn...
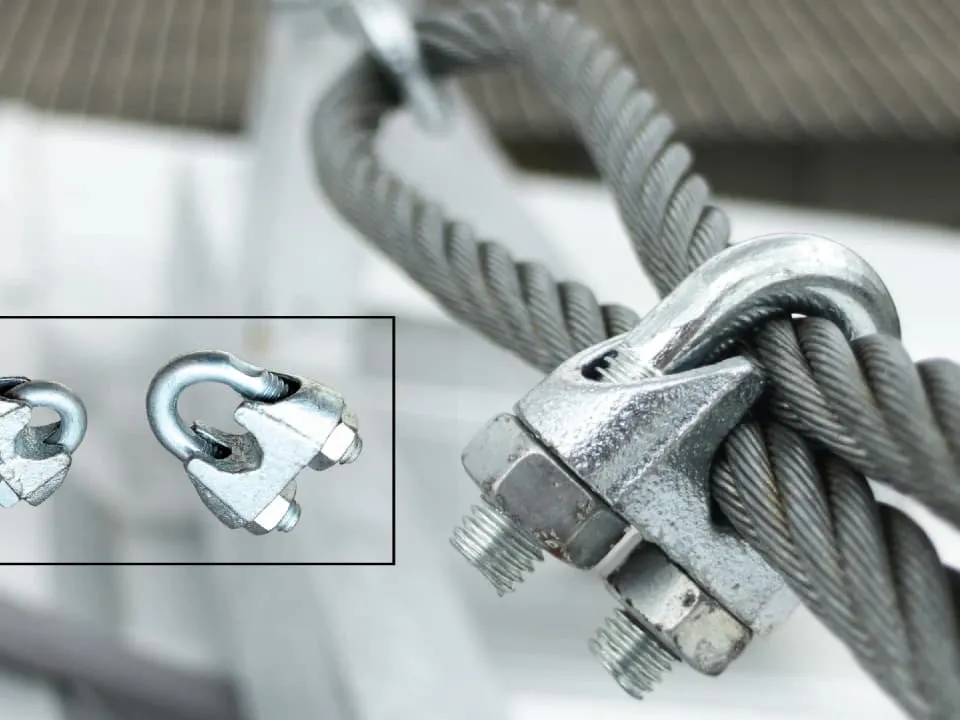
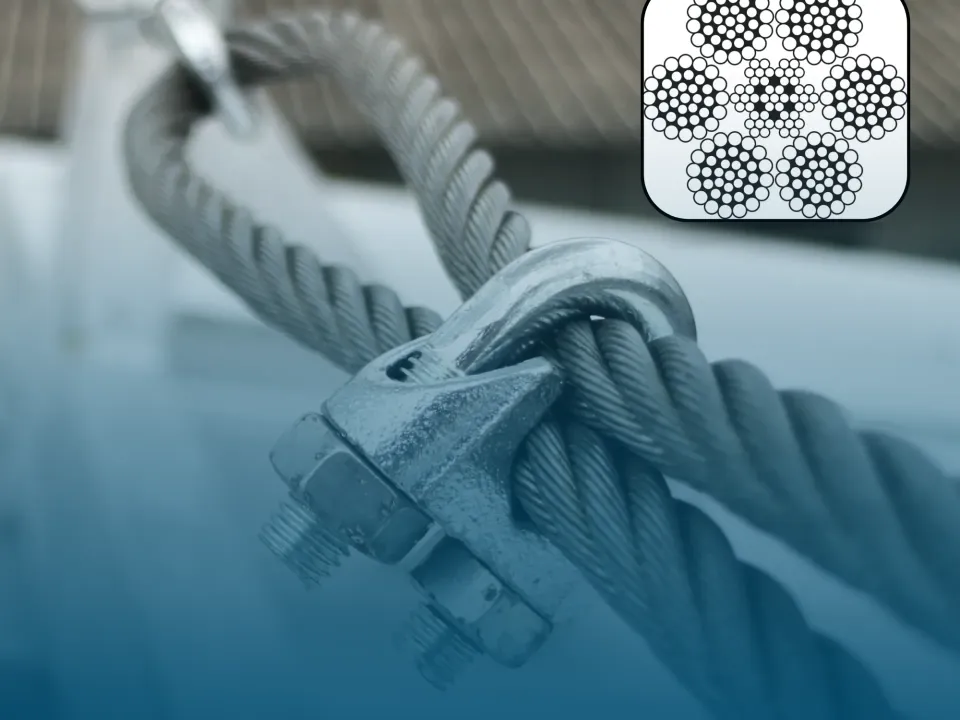
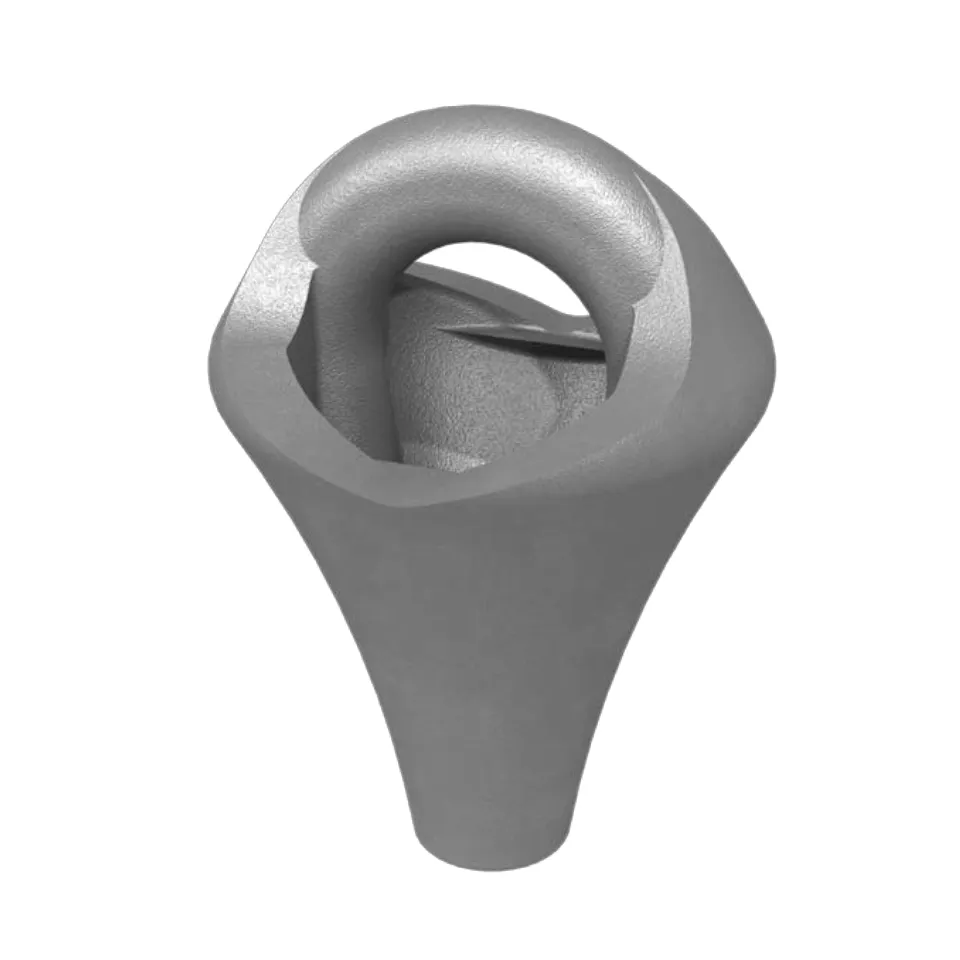
Types of Wire Rope Clips: Functions & Industrial Uses
Discover the different types of wire rope clips and their specific functions in industrial...
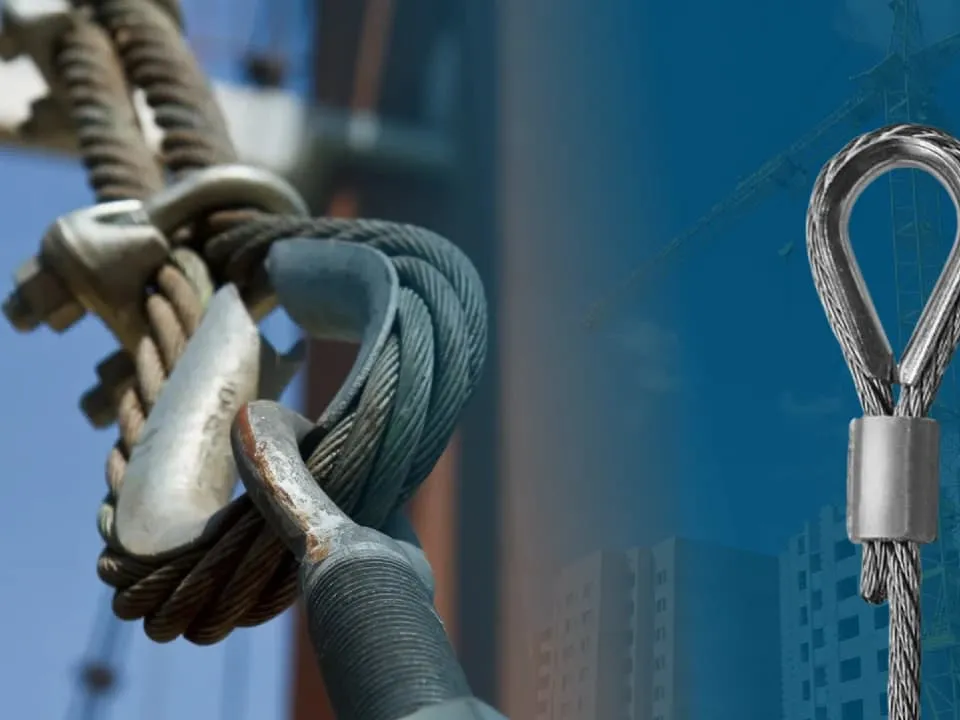
Function of Thimble Sling in Wire Rope Sling: Protection and Safety
Learn the function of a thimble sling in a wire rope sling to maintain strength, prevent wear, and...
Regular maintenance ensures optimal wire rope performance and extends its lifespan. So, what are the...
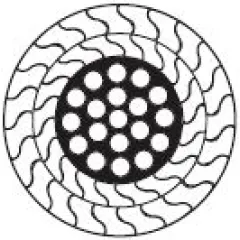
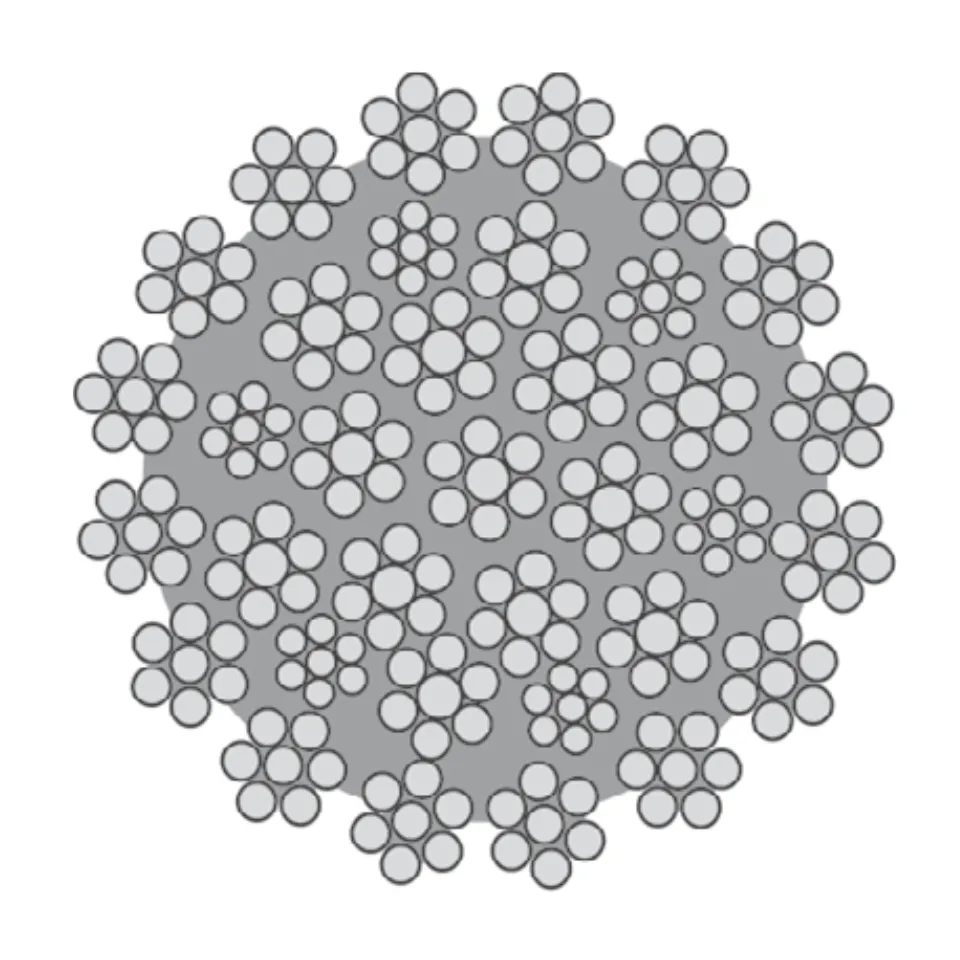
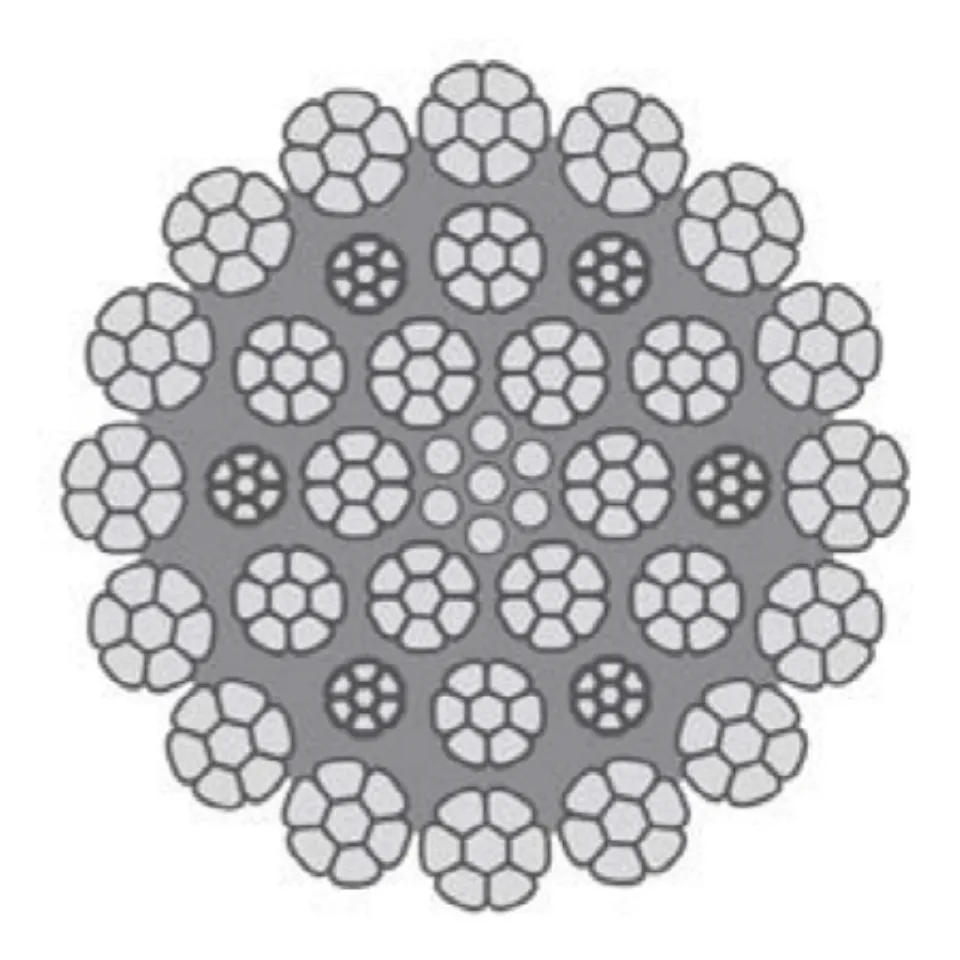
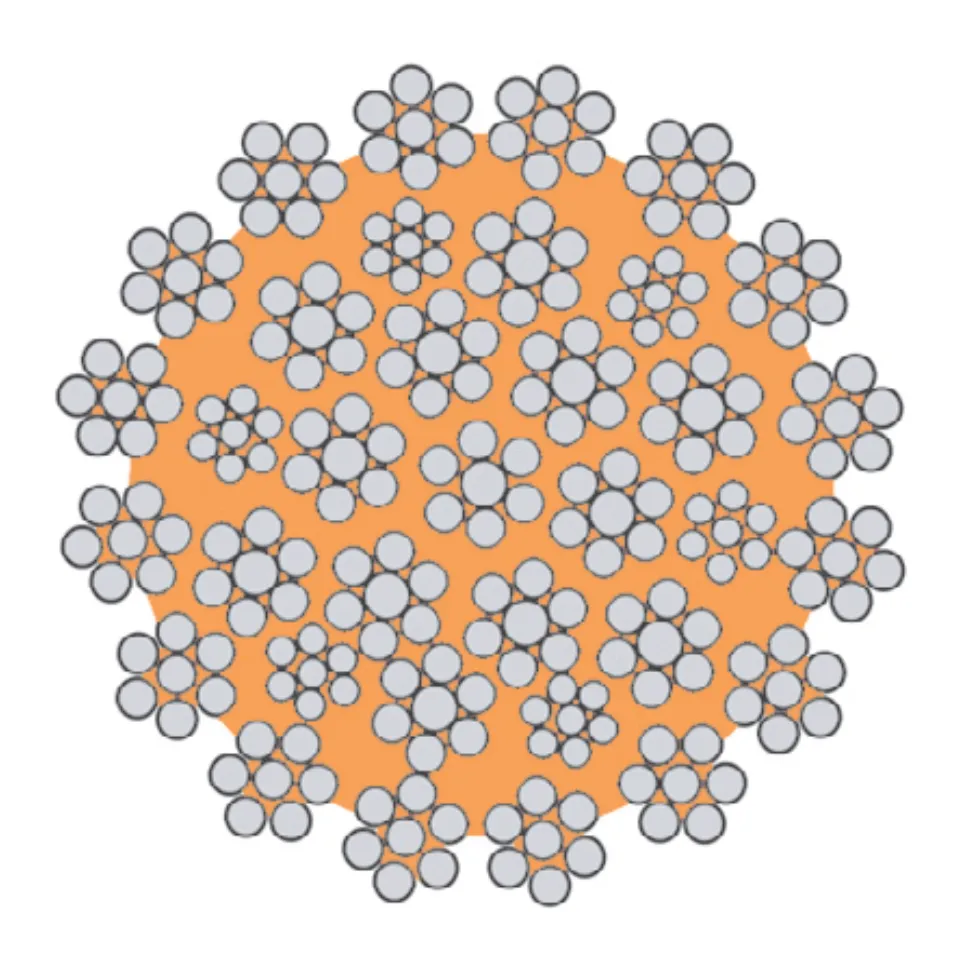
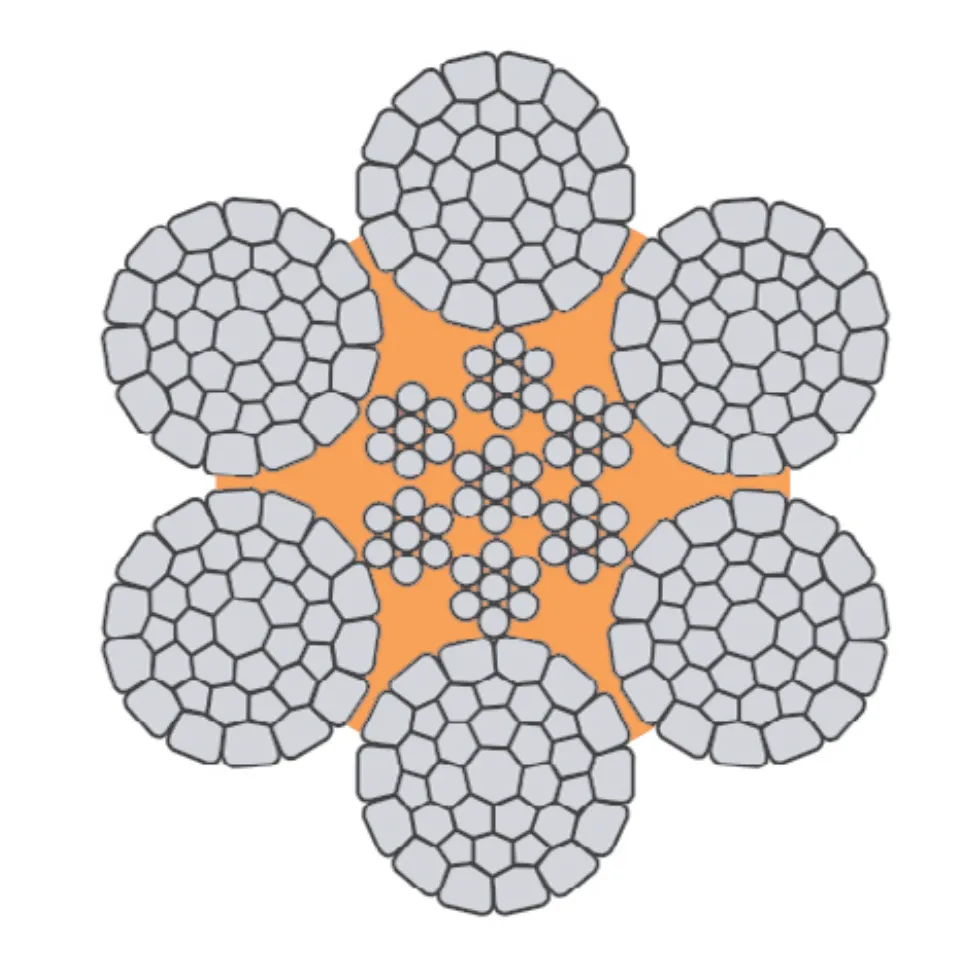
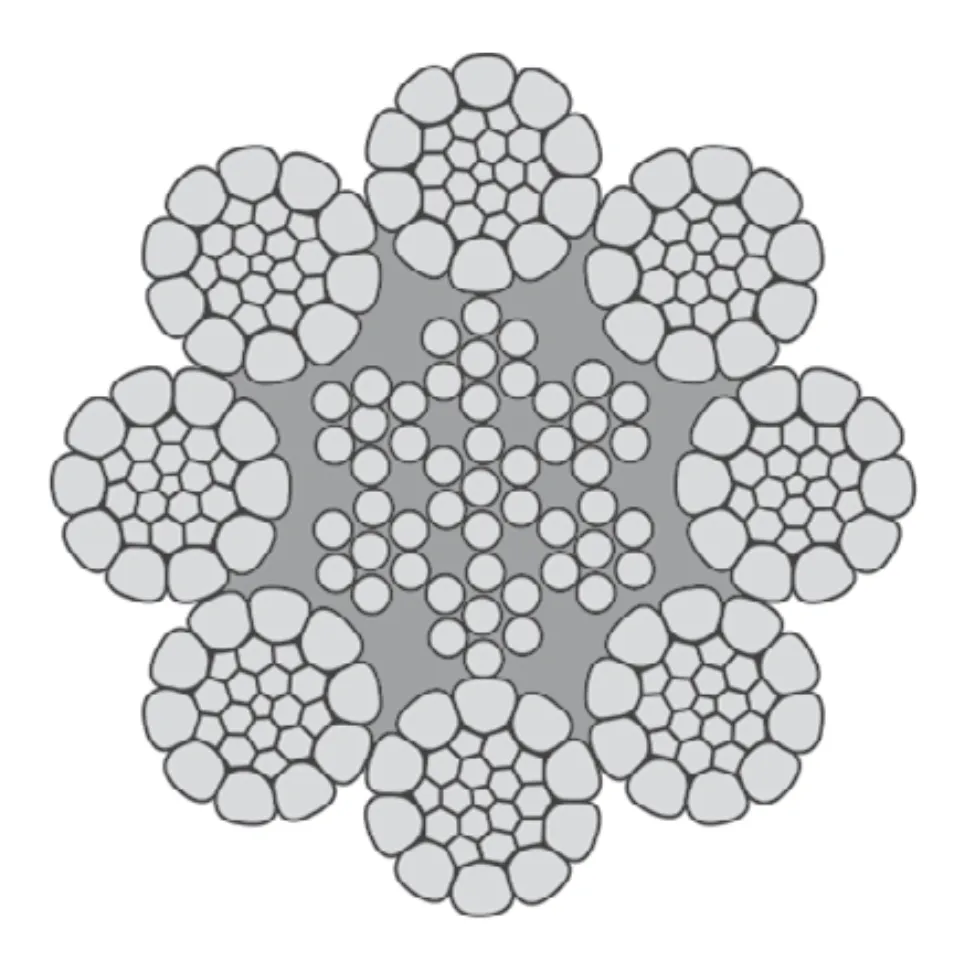
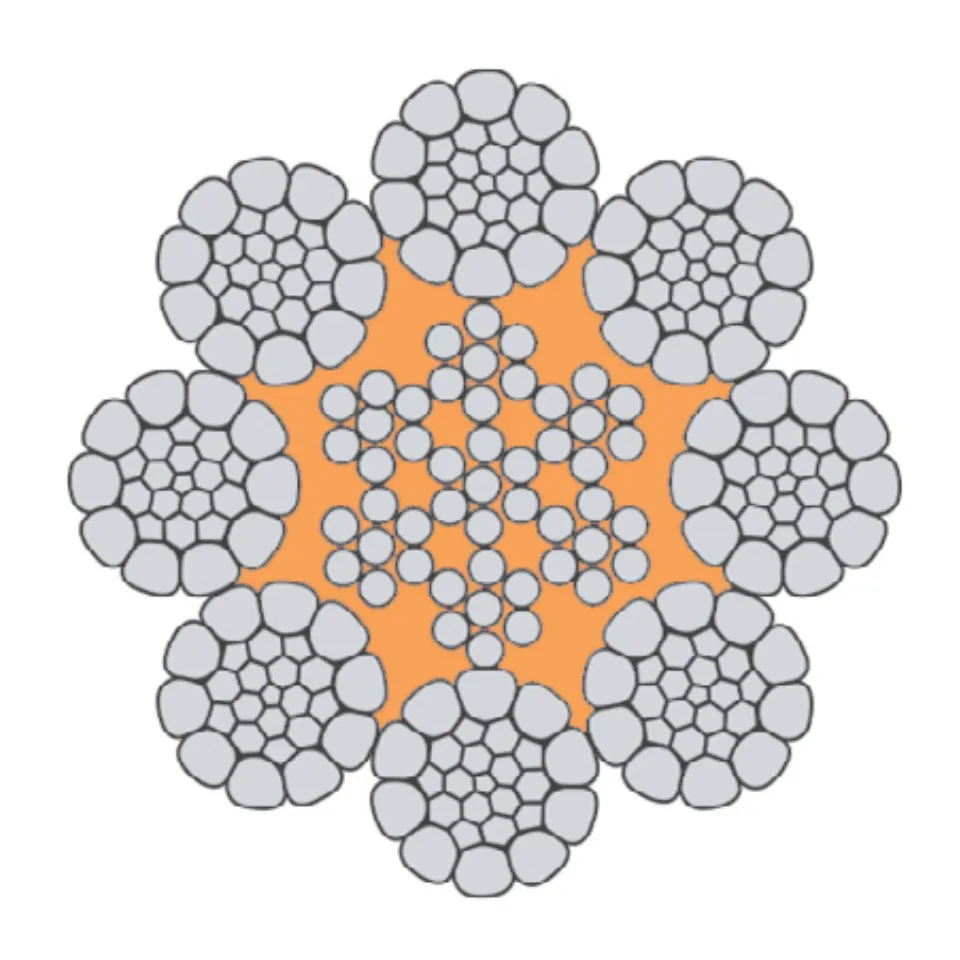
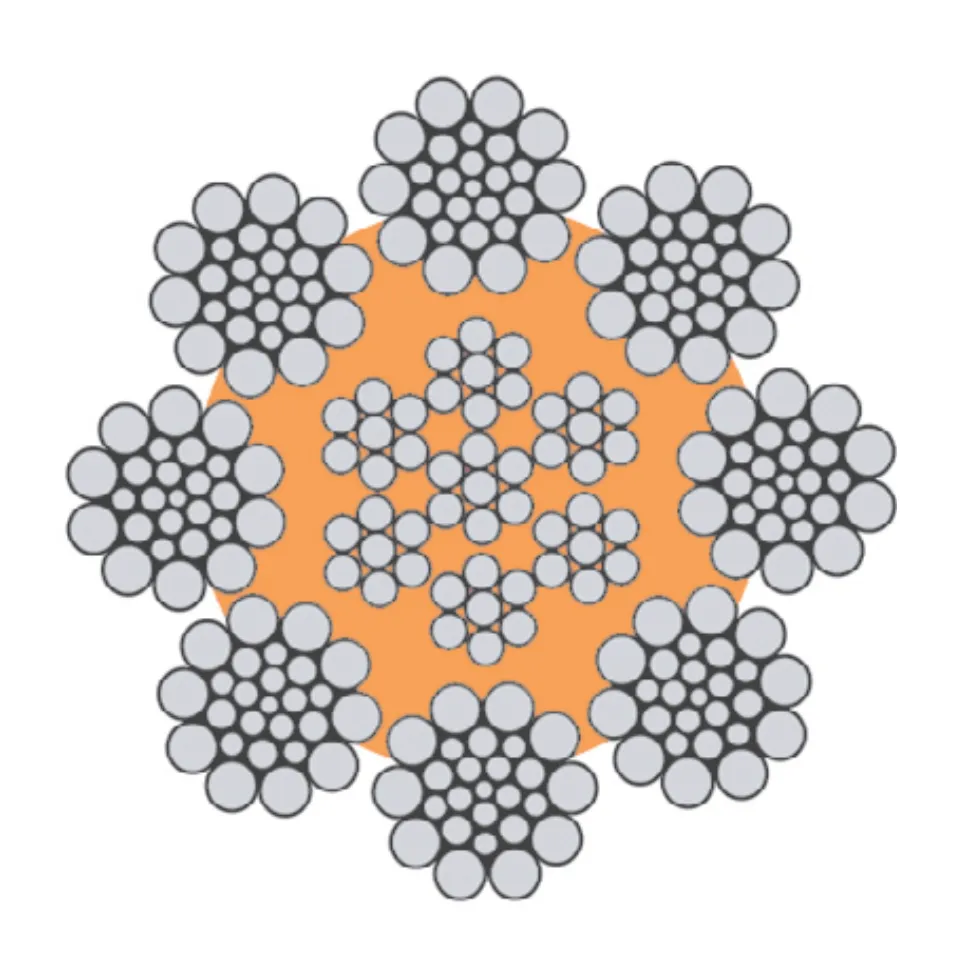
Understanding Wire Rope and Its Types
Wire rope is a steel cable made up of several small wires twisted together. This structure makes it...
Differences Between Wire Rope Sling and Webbing Sling
There are two types of slings that are most commonly used, wire rope slings and webbing slings. This...
Get to Know Wire Rope and its Functions in Various Industries
Wire rope is a rope made of wire that has high strength to withstand heavy loads. Here are its...
Wire Rope IWRC: What Does It Mean? Find Out Here!
Wire Rope IWRC is a type of wire rope that is popular for its strength and durability. Learn more...
Wire Rope Breaking Load: Meaning & Calculation
The breaking load is the maximum tensile force a wire rope can withstand before failure. It depends...
How to Measure Wire Rope Size Correctly
The size of a wire rope affects lifting strength. Learn the correct way to measure wire rope...
Copy of Types of Wire Rope Slings and Their Applications
Guide to selecting wire rope accessories like shackles, sockets, and clips. Ensure safe and...
Types of Wire Rope Slings and Their Applications
Learn the different types of wire rope slings like eye & eye, endless, and bridle slings. Find the...
Types of Wire Rope Damage & How to Prevent Them
Discover common wire rope damage—rust, broken wires, diameter reduction, and more—and learn...
Types of Wire Rope Clips: Functions & Industrial Uses
Discover the different types of wire rope clips and their specific functions in industrial...
Function of Thimble Sling in Wire Rope Sling: Protection and Safety
Learn the function of a thimble sling in a wire rope sling to maintain strength, prevent wear, and...
Regular maintenance ensures optimal wire rope performance and extends its lifespan. So, what are the...
Understanding Wire Rope and Its Types
Wire rope is a steel cable made up of several small wires twisted together. This structure makes it...
Differences Between Wire Rope Sling and Webbing Sling
There are two types of slings that are most commonly used, wire rope slings and webbing slings. This...
Get to Know Wire Rope and its Functions in Various Industries
Wire rope is a rope made of wire that has high strength to withstand heavy loads. Here are its...
Wire Rope IWRC: What Does It Mean? Find Out Here!
Wire Rope IWRC is a type of wire rope that is popular for its strength and durability. Learn more...